GLUETACS co-published a research paper on BCL-xL degrader displaying synergistic antitumor effects on hepatocellular carcinoma
ON:2024-09-24 TAGS:GLUETACS THERAPEUTICS
Recently, Gluetacs Therapeutics and Tan Wenfu lab from Fudan University published an article titled “Sorafenib and SIAIS361034, a novel PROTAC degrader of BCL-xL, display synergistic antitumor effects on hepatocellular carcinoma with minimal hepatotoxicity” online in the prestigious international journal Biochemical Pharmacology. The article reports that SIAIS361034, a PROTAC degrader targeting BCL-xL protein, selectively degrades BCL-xL protein in liver cancer cells. When combined with sorafenib, it exhibits excellent safety and potent antitumor effects in the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma.
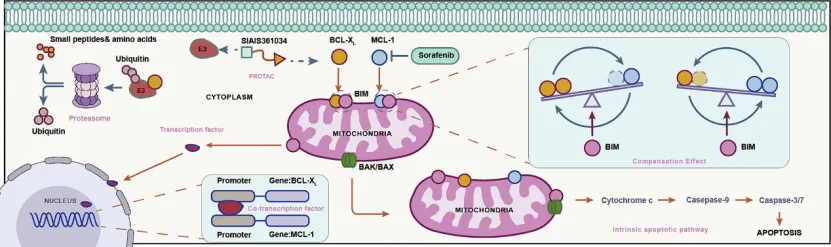
Figure 1
BCL-xL, a mitochondrial transmembrane molecule and a member of the anti-apoptotic BCL-2 family of proteins, plays a crucial role in regulating mitochondrial apoptosis. The research team first compared the expression differences between two anti-apoptotic proteins, BCL-xL and MCL-1, in tumor public databases. High expression levels of BCL-xL mRNA are closely related to poor prognosis in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Compared to MCL-1, BCL-xL mRNA may be a more important indicator of hepatocellular carcinoma progression. Although previous combined therapeutic strategies targeting BCL-xL and MCL-1 have shown some clinical efficacy, they are associated with significant hepatotoxicity. Therefore, addressing the hepatotoxic side effects resulting from co-targeting MCL-1 and BCL-xL is crucial.
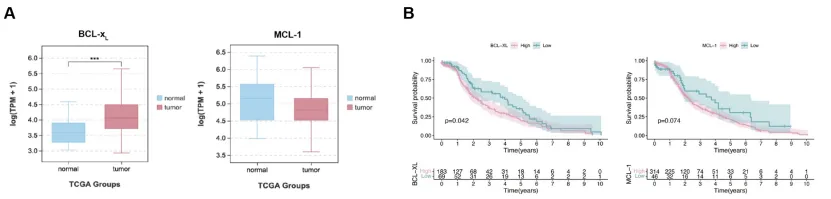
Figure 2 BCL-xL expression and survival analysis in liver cancer
In previous research, Gluetacs Therapeutics and Tan Wenfu lab developed the compound SIAIS361034 using PROTAC technology, which can selectively degrade BCL-xL protein. The research team first examined the anti-proliferative activity of SIAIS361034 in combination with sorafenib, which can downregulate MCL-1, on liver cancer cells and normal liver cells. The results showed that SIAIS361034 combined with sorafenib synergistically inhibited the proliferation of liver cancer cells but had no significant anti-proliferative activity against normal liver cells.
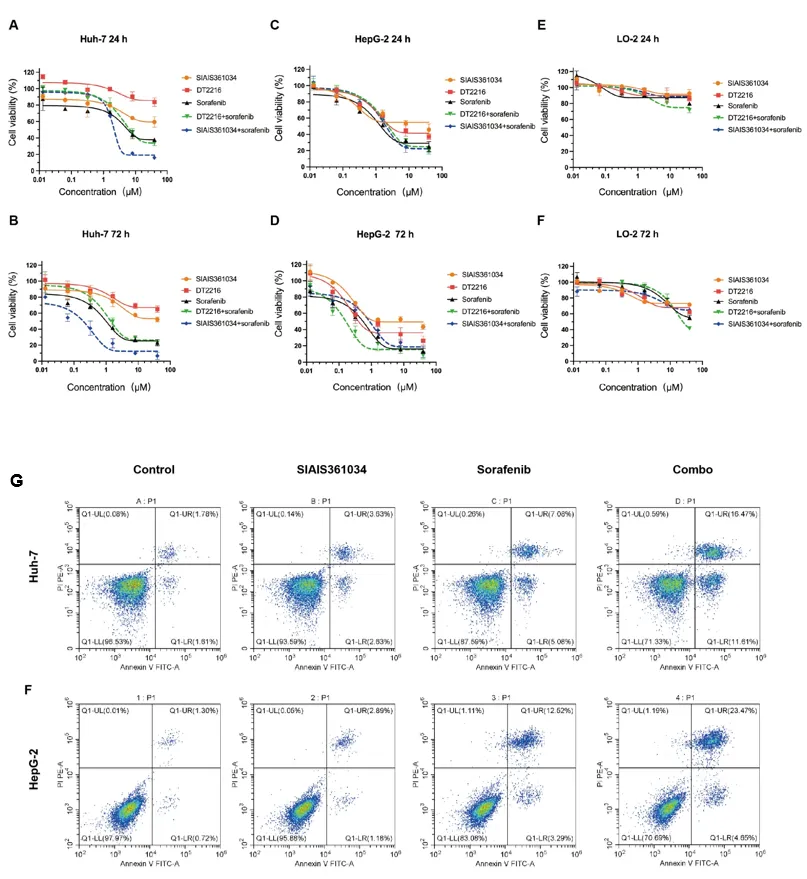
Figure 3 Combination SIAIS361034 and Sorafenib displays synergistic effects on apoptosis with minimal hepatotoxicity
To further evaluate the antitumor effects of SIAIS361034 combined with sorafenib, the research team established a xenograft model of liver cancer. It has been demonstrated that PROTAC compounds targeting BCL-xL exhibit superior anti-tumor activity and better tolerability in liver cancer compared to traditional small molecule inhibitor when combined with sorafenib. This may be attributed to the differential expression of CRBN in normal liver tissue and liver cancer cells. Compared to normal tissue, PROTAC molecules targeting BCL-xL are more likely to degrade BCL-xL in liver cancer cells, so the combination of sorafenib did not show significant toxicity.
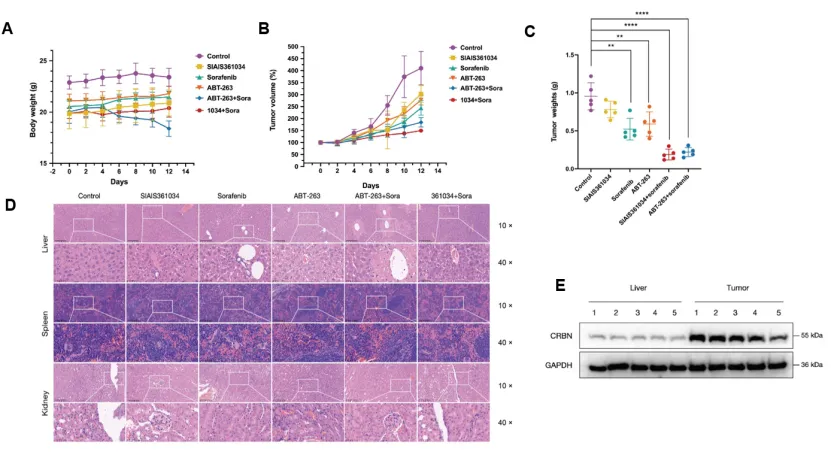
Figure 4 Combination SIAIS361034 and Sorafenib displays synergistic antitumor effects on hepatocellular carcinoma with minimal hepatotoxicity
In summary, the research team found that the PROTAC compound targeting BCL-xL combined with sorafenib exhibits excellent antitumor activity against liver cancer, with better tolerability and safety compared to traditional small molecule inhibitor.
Gluetacs Therapeutics, by publishing this article with academic institutions as a corresponding affiliation, has once again demonstrated the rich technical reserve and translational potential of the GlueTacs® platform, as well as its significant academic valuation and commercial potential.
《Biochemical Pharmacology》linking
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0006295224005422